
When the assembly line was introduced, industrial productivity increased by tenfold. Placing sets of eyes next to each other systematically allowed workers to dedicate their attention on one portion of the process, utilizing specialization to increase the overall efficiency in a factory. As revolutionary as it was, we soon realized that humans were prone to exhaustion on an assembly line, and as a result, were also prone to mistakes. So, we went back to the drawing board to put new and improved sets of “eyes” on the line, and we came back with Machine Vision.
From driverless cars to autonomous farming, machine vision has become an integral part of many automated systems. According to a study from 2017, the global machine vision market was valued at $7.91 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach a whopping $12.29 billion by 2023. Integrating AI into industrial machine vision software enables deep learning in robotics technology, and as such, is set to be one of the fastest growing segments between now and 2023.
The growth in machine vision investment can be attributed to several factors, including factories’ needs for quality inspection and automation; a growing demand for AI and IoT (Internet of Things)-integrated systems that depend on machine vision; an increasing adoption of Industrial 4.0 technologies (referring to the Fourth Industrial Revolution) that rely on machine vision to improve the productivity of robotic automation; and government initiatives to support smart factories around the world.
With a globally increasing desire for machine vision-enhanced processes, there are several current trends that pervade the market:
1. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Connecting production technology with information technology in factories to increase productivity. This depends heavily on machine vision to collect information and is often used for predictive maintenance and/or optimizing business processes. An IIoT system will consist of intelligent assets (i.e. applications, controllers, sensors, and security components that can detect, communicate and store information about themselves); data communications infrastructure (e.g. the cloud); analytics and applications to generate business information from raw data; and people.
2. Non-Industrial Application: Including driverless cars, autonomous farm equipment, drone applications, intelligent traffic systems, guided surgeries, and other non-industrial uses of machine vision.
3. Ease of Use: PC-based machine vision systems will remain popular despite their age, simply due to their ease of use. The desire for an easier interface may push for standardization within machine vision products, making them more practical and accessible both inside and outside factory environments.
Applications of machine vision have been especially helpful to factories where repeated processes need to be fulfilled quickly and with precision. At PepsiCo., machine learning and vision have proven to be a perfect fit. Shahmeer Mirza, the senior research and development engineer at PepsiCo., has been building systems to guarantee the quality of Frito-Lay chips. “One of my first projects at the company involved building systems that could sense the texture of chips without destroying them,” said Mirza. For this project, he was capturing acoustic data and manually processing it. “It’s a system that hits the chip with lasers, listens to the sound coming off them, and then uses that data to correlate the sound into texture.”
By combining the principles of machine learning with computer vision technology, Mirza has since developed more advanced sensors and process control schemes. Specifically, he has created a machine learning model that would work with a vision system to calculate the weight of the potatoes being processed. The idea was to build a model that could predict their weight just by looking at their images.
In addition to predicting weight, Frito-Lay also uses a vision system to look at the peeling process. With the help of the system, the factory can optimize the peeling to a desired percentage so that no potato flesh is peeled away and wasted. Thanks to this optimized peeling process, the project is estimated to save the company over a million dollars a year in the U.S. alone.
In the world of manufacturing, machine vision can significantly help a company with their Asset Maintenance, of which there are four strategies:
1. Reactive Maintenance: Slowdowns and failures are addressed as they arise.
2. Preventive Maintenance: Equipment maintenance is performed on a pre-planned schedule, replacing and maintaining parts before failure is possible.
3. Predictive Maintenance: Using machine learning and IIoT devices to monitor data on machinery and components, often with sensors collecting data points, identifying signals or taking corrective actions before assets or components break down.
4. Prescriptive Maintenance: Equipment operation is continuously monitored with sensors, and all real-time and historical data is analyzed by advanced software to prescribe specific maintenance activities, ensuring optimal equipment uptime.
Machine vision can be found in various parts of production, including packaging inspection, reading barcodes, product assembly, defect reduction, 3D vision inspection, and many more. Machine vision, combined with deep learning systems, are also prevalent in everyday environments including traffic monitoring, sports analytics, bottle recycling, precise medical procedures, and more.
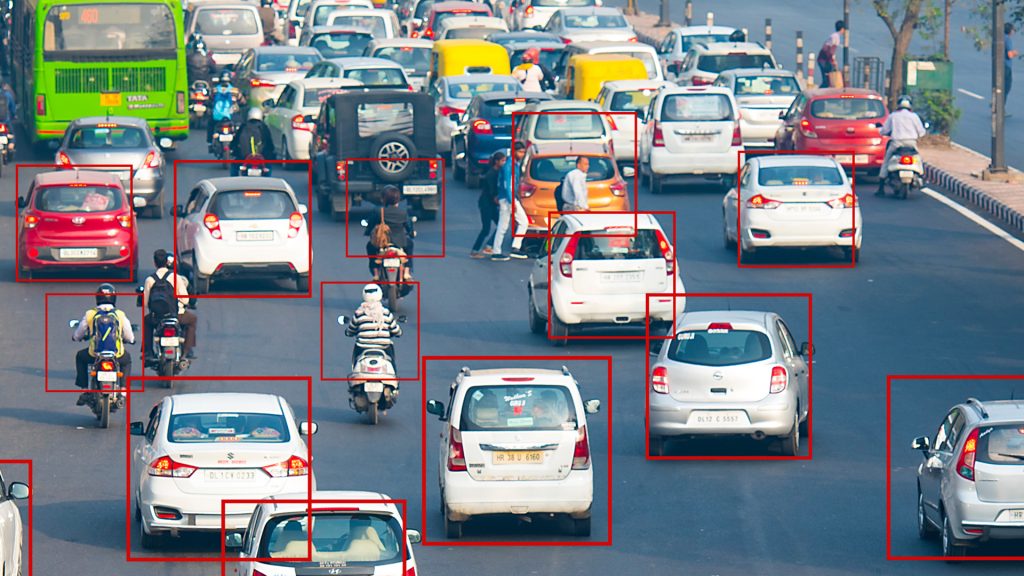
As with most production technologies, one of the main reasons for a factory to upgrade their equipment is for cost-effective results, which machine vision ought to do with the right learning model and vision system. Investing in an AI-integrated machine vision software enables deep learning in robotics technology and can significantly cut down on maintenance costs while improving efficiency.
With automation on the rise, machine vision helps to monitor every step of a production process and can provide data and feedback on the efficiency of an automated system. Even as automation and AI improve, we will always need a set of eyes to tell us if something is working, and where we can improve.
Immersive Experiences: The Changing Landscape of Live Entertainment
Automation Anxiety: AI and Creativity


Andrew Gordon is the Vice President of Business Development at CAST Group of Companies. A strong proponent of innovation with over 15 years of experience, he has helped expand company objectives and exceed business goals. With BlackTrax Real-Time Tracking and CONVRG under his sleeve, Andrew is an expert in his field of automation and live entertainment technologies. An avant-garde early tech adopter, Andrew has become a trailblazer in the industry with an instinctual knack for foreseeing trends. As a highly motivated and forward-thinking individual with a big picture approach, Andrew has had the opportunity to work hand-in-hand with world-renowned brands such as Feld Entertainment, Cirque du Soleil and Disney, as he propels the team at CAST Software to record heights. With the belief that “Everything is and should be interconnected with tracking and automation at the centre of it all,” Andrew’s development skills and innovative ideas continue to surprise the industry.
Read Full Profile© 2021 TheatreArtLife. All rights reserved.

Thank you so much for reading, but you have now reached your free article limit for this month.
Our contributors are currently writing more articles for you to enjoy.
To keep reading, all you have to do is become a subscriber and then you can read unlimited articles anytime.
Your investment will help us continue to ignite connections across the globe in live entertainment and build this community for industry professionals.